Absolutely! Here’s a 2700-word article about “painting the tape” in finance, with list items converted to headings (either
or
, depending on the context).
“Painting the tape” is a term that evokes images of old trading floors, where ticker tape streamed across screens, displaying stock prices. While the physical tape is largely obsolete, the practice it describes—manipulating market prices through artificial trading activity—remains a concern in modern financial markets. Understanding this tactic is crucial for investors, regulators, and anyone involved in the financial ecosystem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-881879106-aa07d4824acc40adaece64531b347875.jpg)
Painting the tape refers to the act of creating a misleading impression of market activity. This is achieved by executing a series of trades, often near the end of a trading session, to artificially inflate or deflate the price of a security. The goal is to influence investor perception and, ultimately, their trading decisions.
How exactly does this manipulation occur? Several techniques can be employed:
Wash Trades and Matched Orders
These involve an individual or a group of individuals simultaneously buying and selling the same security among themselves. This creates the illusion of high trading volume and price movement, without any genuine change in ownership.
Marking the Close
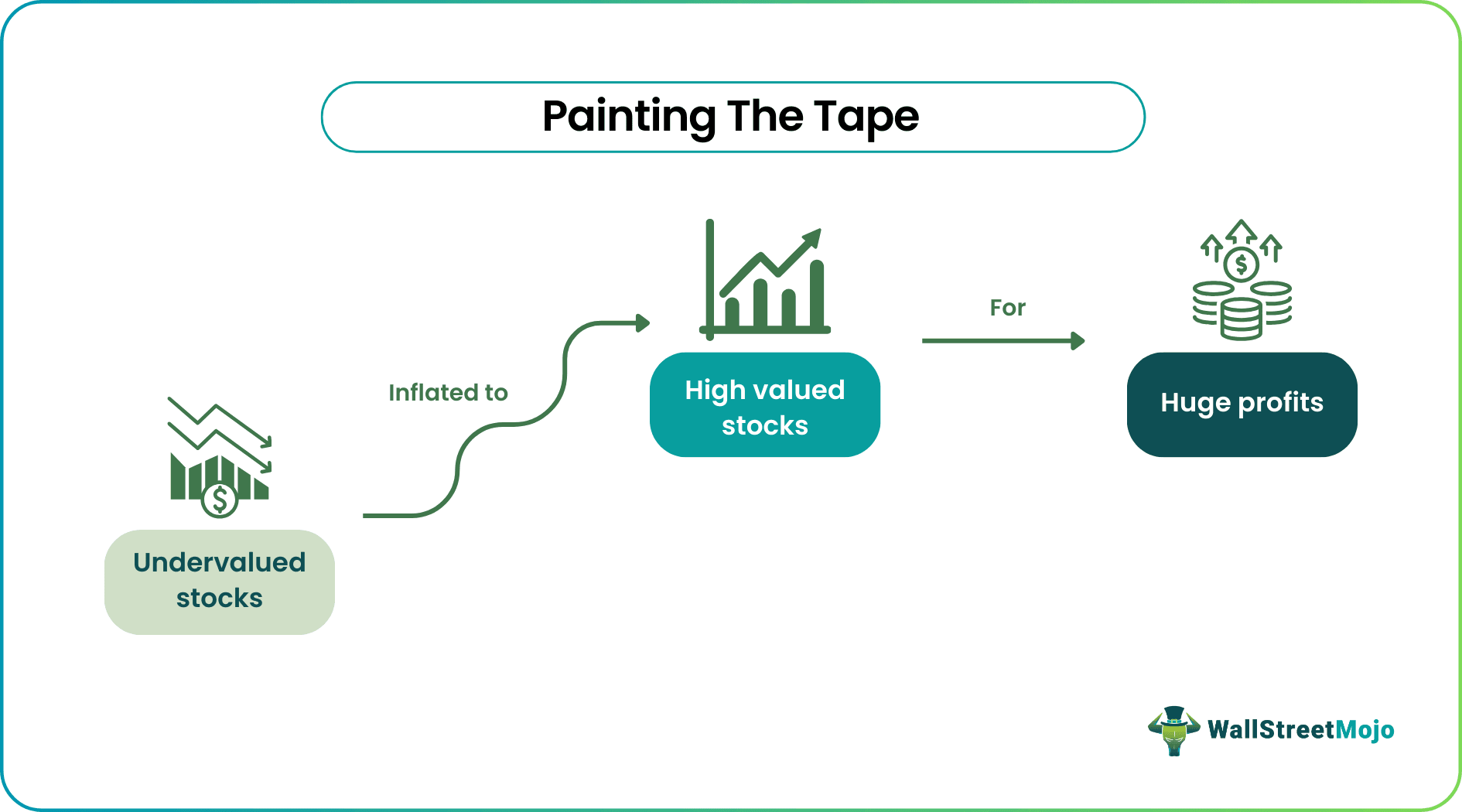
This tactic involves placing large buy or sell orders just before the market closes. These orders are intended to push the closing price of a security in a desired direction. This can impact the valuation of portfolios and derivatives that rely on closing prices.
Layering and Spoofing
These more sophisticated techniques involve placing and quickly cancelling orders to create a false sense of supply or demand. This can trick other market participants into reacting to the artificial signals, allowing the manipulator to profit.
Why would someone engage in such manipulative practices? The motivations are varied and often intertwined:
Inflating Portfolio Values
Fund managers may attempt to inflate the value of their holdings to enhance their performance reports. This can attract new investors and justify higher fees.
Triggering Stop-Loss Orders
Manipulators may aim to drive a security’s price below a certain level to trigger stop-loss orders. This can create a cascade of selling, allowing them to buy the security at a lower price.
Manipulating Options Prices
Painting the tape can influence the prices of options contracts, which are derivatives whose value is tied to the underlying security. This can create opportunities for arbitrage or outright manipulation of options markets.
Creating a False Sense of Momentum
By artificially driving up a stock’s price, manipulators can create a perception of momentum, attracting other traders who are looking to jump on a perceived trend.
Painting the tape undermines the integrity of financial markets. It distorts price discovery, reduces market efficiency, and erodes investor confidence. The consequences can be significant:
Loss of Investor Trust
When investors believe that prices are being manipulated, they are less likely to participate in the market. This can reduce market liquidity and increase volatility.
Distorted Price Discovery
Manipulated prices do not reflect the true value of a security. This can lead to misallocation of capital and inefficient investment decisions.
Increased Market Volatility
Artificial price movements can lead to increased volatility, making it more difficult for investors to manage risk.
Regulators around the world are aware of the dangers of painting the tape and have implemented measures to combat it. However, detecting and prosecuting these practices can be challenging:
Surveillance Technology
Regulators use sophisticated surveillance technology to monitor trading activity and identify suspicious patterns.
Enhanced Reporting Requirements
Increased transparency and reporting requirements can help to deter manipulative practices.
Cross-Market Surveillance
As markets become more interconnected, regulators are increasingly collaborating across jurisdictions to monitor trading activity.
Challenges in Proving Intent
Proving that a trader intended to manipulate the market can be difficult. Regulators often rely on circumstantial evidence and trading patterns to build their cases.
Technology plays a dual role in painting the tape. While it can be used to facilitate manipulation, it also provides tools for detection and prevention:
Algorithmic Surveillance
Sophisticated algorithms can analyze vast amounts of trading data to identify patterns that suggest manipulation.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning can be used to detect anomalies and predict potential manipulation attempts.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in financial transactions, making it more difficult to manipulate prices.
Examining real-world cases can provide valuable insights into the mechanics and consequences of painting the tape:
Historical Examples
Numerous historical cases illustrate the prevalence of painting the tape. From the early days of the stock market to more recent scandals, the practice has been a persistent problem.
Modern Examples
Even in today’s highly regulated markets, cases of alleged manipulation continue to surface. These cases often involve complex trading strategies and sophisticated technology.
International Cases
Painting the tape is not limited to any one jurisdiction. Cases have been reported in markets around the world, highlighting the global nature of this problem.
While regulators work to combat manipulation, investors can take steps to protect themselves:
Due Diligence
Thoroughly research the securities you are considering investing in. Understand the company’s fundamentals and the market dynamics.
Diversification
Diversify your portfolio across different asset classes and sectors to reduce your exposure to any single security or market.
Limit Orders
Use limit orders to control the price at which you buy or sell securities. This can help to protect you from sudden price swings.
Be Wary of Unusual Volume
Pay attention to sudden and unexplained increases in trading volume. This could be a sign of manipulation.
Stay Informed
Keep up to date on market news and regulatory developments. This can help you to identify potential risks and opportunities.
As financial markets continue to evolve, the challenges of maintaining market integrity will persist. However, ongoing advancements in technology and regulation offer hope for a more transparent and equitable marketplace:
Enhanced Regulatory Cooperation
Increased collaboration among regulators across jurisdictions will be crucial in combating cross-border manipulation.
Technological Innovation
Continued investment in surveillance technology and AI-driven detection tools will be essential.
Investor Education
Empowering investors with knowledge and tools to protect themselves is a critical component of market integrity.
Ethical Considerations
Promoting a culture of ethical behavior within the financial industry is paramount.
Painting the tape is a serious form of market manipulation that undermines the integrity of financial markets. While regulators and technology play important roles in detection and prevention, investors must also remain vigilant. By understanding the mechanics of this practice and taking steps to protect themselves, investors can contribute to a more transparent and equitable marketplace. The ongoing pursuit of market integrity is a collective responsibility, ensuring that financial markets serve their intended purpose: to facilitate the efficient allocation of capital and promote economic growth.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-881879106-aa07d4824acc40adaece64531b347875.jpg)